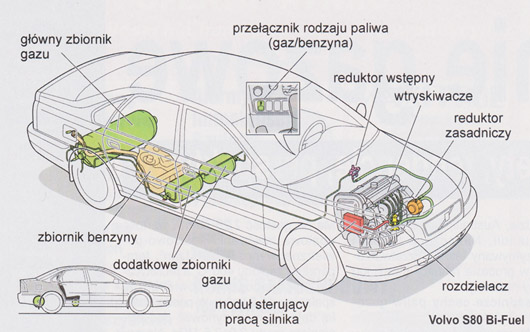
 LPG gas has a density 2,25 kg/m3, the calorific value of the air-fuel mixture is 3,39 MJ / m3, flash point 400 ° C, a theoretical combustion air requirement – 15,5 kg / kg. It can be stored in liquid form under a pressure of the order 2,0-2,5 MPa. In the early years 90. annually used to drive vehicles around the world. 8,2 million tons of liquid gas, of which approx. 2,5 million tons in Europe (mainly Italy and the Benelux countries). Natural gas (density 0,695 kg/m3, calorific value 3,4 MJ / m3, air demand 9,5 kg / kg) requires storage after condensation in a cooled container at -160 ° C or after compression under pressure 16-20 MPa. It is most popular in the USA, New Zealand, Argentina, Italy and Russia. There are approx. 1 min such vehicles. The design of the power supply system and the composition of exhaust gases are similar for LPG and CNG / LNG, the differences lie in the construction of the tank.
LPG gas has a density 2,25 kg/m3, the calorific value of the air-fuel mixture is 3,39 MJ / m3, flash point 400 ° C, a theoretical combustion air requirement – 15,5 kg / kg. It can be stored in liquid form under a pressure of the order 2,0-2,5 MPa. In the early years 90. annually used to drive vehicles around the world. 8,2 million tons of liquid gas, of which approx. 2,5 million tons in Europe (mainly Italy and the Benelux countries). Natural gas (density 0,695 kg/m3, calorific value 3,4 MJ / m3, air demand 9,5 kg / kg) requires storage after condensation in a cooled container at -160 ° C or after compression under pressure 16-20 MPa. It is most popular in the USA, New Zealand, Argentina, Italy and Russia. There are approx. 1 min such vehicles. The design of the power supply system and the composition of exhaust gases are similar for LPG and CNG / LNG, the differences lie in the construction of the tank.
Power methods:
• mieszanka palna może powstawać w mieszalniku, to which the gas from the tank is fed through a pressure reducer;
• gaz sprężony o wysokim ciśnieniu jest wtryskiwany do kanału dolotowego lub bezpośrednio do cylindra;
• skroplony gaz jest wtryskiwany do cylindra.
It is technically feasible to adapt any gasoline engine (both carburetor powered, and injection molded) for gas propulsion (start-up or emergency access to a petrol or diesel fuel dispenser). In general, it is possible to switch from one type of fuel to another. Increase in consumption (half the price!) fuel is on average 10-15% in the case of injection system i 15-20% carburetor system. Is estimated, that the depreciation time for a vehicle equipped with a gas system is approx. 2 patch. Natural gas is also cheaper, but the cost of vehicle adaptation is higher. LPG or CNG are predominantly used in passenger cars, in utility – LNG. LPG is easier to store, but as it is heavier than air, it can accumulate on the ground in the event of pipe leakage, run into drains and cause an explosion. In some countries, this led to a ban on parking gas-powered cars in underground garages.
DISADVANTAGES OF GAS POWER
Disadvantages of gas drives compared to traditional ones (gasoline / diesel):
• mniejszy zasięg przy tej samej masie paliwa (np. 55 dm3 of gasoline is equivalent 105 dm3 LPG i 244 dm3 CNG);
• konieczność przestrzegania szczególnych warunków bezpieczeństwa (high pressure);
• smaller luggage compartment capacity due to the gas tank (cylindrical or toroidal) mostly with capacity 40-128 dm3, filled to 80% volume.